—
 |
| The fateful date. Sometimes numbers can be converted, and acquire additional meaning. |
—
This chapter is devoted to the conversion of quantities. This is, what turns psychology into an exact science, and makes it possible both to produce a quantitative analysis of the psychology of a living being, and to create own living beings.
—
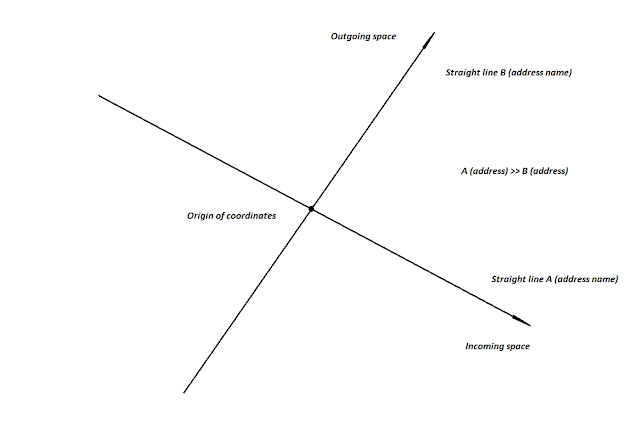
The conversion of quantities is the transfer (reflection, projection) of a point from one straight line to another. The line, from where the point needs to be reflected, is called the incoming space, and the line, where the point needs to be reflected, is called the outgoing space. Geometrically, we can imagine a point A, which is located at the intersection of two lines, where each line is a dedicated space, that has its own name. Point A is located on every straight line, it is an incoming point in each space and the origin of coordinates. If there is an outgoing point in the incoming space, from which a straight line segment of length AB can be formed, then the outgoing point B can be reflected into the outgoing space. After the transfer, point B on the outgoing line will have a different coordinate (y) relative to point A. The correspondence of the incoming and outgoing spaces is called an association, it also includes the correspondence of the position of point B in these spaces relative to the common center of A.
In addition to the namespace (the name of each line), the conversion consists of logic and quantities (coordinates). The latter are the lengths of straight line segments (or coordinates (x) and (y)), where one of the ends of the segment and the origin of coordinates is the incoming point A, relative to which point B has coordinates (x) and (y)). The magnitude transformation is the conversion of the coordinate (x) into the coordinate (y), which correspond to each other, because they are in associated spaces and belong to the same point B, but are not necessarily equal in magnitude, the magnitude of the outgoing definition (coordinate (y)) is calculated by a given function as a derivative of the magnitude of the incoming definition (coordinates (x)). Logic skips the transfer from one definition to another in the sequence itself, whether the value can be converted or not.
—
A mathematical point (point A in our example, this is a living being and its selected parameter) is located at the intersection of two straight lines, its coordinate, according to the rules of analytical geometry, is zero. The value of the incoming definition (the length of the line segment) is set by the coordinate of point B relative to point A. Point A divides the incoming line into two parts, and point B can lie to the left or right of point A. In distilled psychology, negative values are not welcome, but in our culture, everything on the left is considered negative coordinates. Point A divides into two parts and the outgoing line, where we should move point B. Here point B can also lie to the left or right of point A. Unlike the usual way of projection (reflection), when the position of a point on the right or left on one straight line should correspond to the position of a point on another straight line, in psychology, the position of a point can be arbitrary from two options. The side of the space, where the point B cannot be located, and where it cannot be reflected, is considered to be the space behind the back, the space behind the back is on both straight lines, and it has a different name (or does not have it at all).
The first in the order is the incoming space (the name of the line), the outgoing point in such a space depending on the direction (this is B or –B) or the coordinate depending on the direction (this is (x) or (–x)), then the outgoing space (the name of the line) is indicated, the reflection of the outgoing point in such a space depending on the direction (it’s B or –B) or the coordinate depending on the direction (it’s (y) or (–y)). The correspondence is not an equality of magnitudes, it is an association of magnitudes (as well as spaces and outgoing points in such spaces), since before the reflection of point B is not yet in the associated space, it has to be moved there, and point B does not yet have a coordinate (y), it has to be assigned. And a small example, if (B >> –B), then it means that point B on the incoming line is defined as being to the right of point A (greater than zero or the value of point A), but is transferred to the outgoing line to the left of point A (less than zero or the value of point A), and for coordinates points B (x >> –y).
—
The conversion of quantities is always sequential and directed, the outgoing point in the incoming space is the cause, and in the outgoing space is the effect, between which there is a certain quantity of time (thanks to this, we share for ourselves the past and the future, as well as their sequence). The value can be converted not once, but several times, in this case the point is transferred first to one space, then from this space to another, etc. With such a complex conversion, the outgoing space in relation to the incoming one becomes incoming in relation to the next outgoing one, etc. Point A remains an incoming point in each space relative to point B, and its coordinate remains zero, but the coordinate of point B will be sequentially converted into some final result.
In psychology, the first space is physical reality, where there are physical phenomena (heat, physical extent of space, density, electricity and other physical properties). Further, a certain quantity of such a phenomenon is converted into an actual incoming definition (temperature, physical distance, hardness and other reflections of physical properties), which has a value of. Further, if necessary, the actual incoming definition is converted into an abstract incoming definition (beauty, danger, attractiveness, nutritional value and other psychological properties). Next, the definition is converted into the quantity of irritation, and each type of irritation has its own name. Next, the quantity of irritation is converted into the work being done (reaction to irritation), which has a magnitude of. Further, the work performed is converted into a physical phenomenon, returning the living being and his actions (the work performed) to physical reality. The conversion of irritation into the work being done is carried out through excitation, where the coordinate transformation is different, therefore, if everything is extremely simplified, as well as buffer irritation and physical properties at the input and output are excluded, then the incoming definition (the magnitude of the irritant) is converted into the outgoing definition (the magnitude of the reaction, the work being done), which is a general view of psychology.
 |
| The outgoing value is dependent on the incoming value. If know the input value, then this is the easiest way to calculate (or design) the output value. |
The machine consists of an engine as a source of actions, transmission and actuating mechanisms and a control system. A control system is a set of control tools, impact and accumulation of information. The means of influence are set not so much by the subject of control, as by the modus operandi of the developer, using the example of human technical culture and a living cell, we can see a gap in the thinking, approaches and technologies of two intelligent species (humanity and the creators of all living things), so they are not interesting to psychology. Similarly, for controls, if specific means, that are not universal (human speech or animal organization) act as such. This does not mean, that we cannot make the machine a part of society, or repeat the animal organization, but with gasoline (or another food source) instead of calories, but even such an organization will exist in the material world of physical phenomena. Therefore, as an incoming quantity, we mean first of all a physical parameter, which is universal and material (real), an animal or social organization (abstract definitions or human speech, where each word (sign) contains a quantity) — this is too artificial. But if pay attention not only to the control tool, but also to the subject of control, then this is the same physical parameter, only at the output. Therefore, as an outgoing value, first of all, a physical parameter is meant. If we consider the outgoing quantity (y) to be a controlled quantity, then the incoming quantity (x) is a control quantity. For example, the velocity of a car (outgoing and controlled physical parameter) is regulated by the temperature difference (incoming and control physical parameter). Any living being is familiar with this, the higher the temperature difference, the faster it is necessary to escape to a safe place, the magnitude of the irritant is converted into the magnitude of the reaction. Since the mathematical model is the same, then in the second place it means the conversion of the incoming definition into the quantity of irritation or the quantity of irritation into the outgoing definition. In the third, the conversion of a real definition into an abstract value (worth or sign). In theory, any conversion of energy into work (for example, a heat engine) is also a conversion of quantities, but such a conversion is not a subject of interest for psychology as a management science. Of interest is the energy (or its imitation), which is converted into a command (signal) to the machine and its executive mechanism to perform some work and some quantity of work. Or convert the incoming signal into an outgoing signal, which will be converted into a command (signal) to the machine and its executive mechanism to perform some work and some quantity of work. Both cases imply some parameter, that we transform, which is also work. Accordingly, there is physical and psychological work, physical work is the work of the executive mechanism, psychological work is a change in the quantity of physical work. In this chapter we will skip the psychological work (conversion of irritation into excitation), since such work uses a different model of conversion of quantities. Therefore, when it comes to the work being done, we are talking about the reaction and its magnitude (physical work), which corresponds to the magnitude of the signal.
—
Each space has a name, that distinguishes one space from another. Accordingly, there are names of incoming and outgoing spaces. The incoming and outgoing spaces have the origin, this is the intersection point of two straight lines. In psychology, at this point there is a living being and its selected parameter, which we want to control. Thus, the definition becomes not only a measurement and a prescription, but also an association, it is the identification of the incoming definition, to which associated space it belongs. If we go back to geometry, where the incoming point is at the intersection of two straight lines, then the association is with which and on which lines to reflect the point. And also their sequence, which line is incoming (first, here we will define the coordinate of point B), and which is outgoing (second, here we will reflect the coordinate of point B).
In the most elementary case of association, one incoming name corresponds to one outgoing name (A is B). Here A is the allocated incoming space, B is the allocated outgoing space. Accordingly, the point is transferred from one straight line to another.
For example, warmth is beautiful, and the quantity of warmth is the quantity of beauty. Accordingly, the greater the temperature difference between the points, the more beautiful the defined point will seem to the defining point. Similarly, to convert the quantity of beauty into the quantity of irritation, beauty is the irritation of beauty (the feeling of beauty), and the quantity of beauty is the quantity of irritation from beauty (the expression of the feeling of beauty). Similarly, to transform irritation into a reaction, for example, irritation from beauty is some action, and the quantity of irritation is the intensity, duration or expression of such an action (work performed). In all the examples, one incoming space corresponds to only one outgoing one, and if we exclude intermediate links, then one incoming definition (temperature difference) corresponds to only one outgoing definition (the quantity of work performed, this is a reaction to the temperature difference). If we want to turn an excavator into a living being, then each of its actions in this case is defined by only one incoming signal. For example, one type of signal is for him to move the bucket, another type of signal is for him to move, a third type of signal is for him to dig, etc., but without a signal he will do nothing, just as any living being does nothing without a command (external irritation), which is observed in practice.
In a more complex case, one incoming name corresponds to a set of outgoing ones (A is a multitude). Here the set is several allocated spaces, each of which can have its own logic. As a rule, this is a variant of detailing. Accordingly, the point is transferred from one straight line to several others.
For example, the allocated space for the color palette at the input can be associated with several allocated spaces at the output (red, blue, yellow, and other set). There is no color in nature, there is a wavelength, but there are lengths of different ranges, which can be given different names. In this case, there is a specification of which color (and which wave range). For this example, only one of the set will be true, which brings us back to the elementary case with unambiguous definitions (one corresponds to one). Only here the outgoing one is selected from the set (only one, the others are false). But it can also be an option with several true. In this case, one incoming name will be associated with several outgoing ones at once. Each of which can be assigned true, and then the incoming definition will become multi-valued. Yoghurts are delicious, healthy, nutritious, and much more. Similarly, for an incoming definition, that defines multiple actions. For an excavator, this would be several actions with one irritant, for example, digging and turning on the radio with a certain volume.
A kind of complex case, if the set of incoming corresponds to one outgoing (the multitude is A). As a rule, this is a variant of generalization. Multiple allocated spaces mean one specific thing. Accordingly, several points from different spaces are transferred to one straight line.
 |
| This is an example similar to the example above, here the outgoing space A is associated with several incoming spaces B, C and D. |
A lot of different colors are the color scheme. However, this is, if they are all true, otherwise the gamma will be recognized as monotonous. The option is simpler, if at least one input is true, which again returns us to the elementary one-to-one. An intermediate option, if several are true enough from the set, or under some additional conditions. For example, several types of trees are enough to generalize them into a forest. Or several different temperatures to generalize them into heat as a phenomenon. In a sophisticated version, each of the sets may have its own logic. Some of the many incoming definitions (as well as all of them) can be called from memory. In this case, the incoming definitions will be an array of both predefined data and for matching with valid definitions. For example, if the incoming valid definition matches the one set from memory. This fragrance is the same fragrance.
The opposite of spaces are addresses. The temperature is measured by a thermometer, and nothing else can be measured with it. If the thermometer has found another point, whose temperature differs from its own, then it is possible to form a straight line segment with such a point to establish the temperature difference (definition). In this case, it makes no sense to create a separate temperature space, because we already have such a space set by the thermometer itself, and we understand, what exactly can come from it (only one), and what cannot come (everything else). This is a variant of peripheral devices (instrumentation, sensory organs), that are pre-configured for some specific definitions. Similarly, for outgoing peripheral devices (actuators, muscle cells), which can be controlled separately. And we often see this case in physiology, where the irritant causes a reaction not of all cells, but of some specific ones, that are associated with this type of irritation. This option is good, because it allows to localize the incoming or outgoing definition, because each device has its own address, and we know where and which device is physically located.
 |
| This is an example, where incoming space A and outgoing space B have addresses instead of a name. This means, that they have some position in the three-dimensional physical reality. |
If we imagine, that we have several light bulbs (these are peripheral devices, models of muscle cells or individuals) and several thermometers (these are also peripheral devices, models of nerve cells or nervous duration of individuals), then any association by name will connect us thermometers and light bulbs, the work of the latter (turn on the lighting) will be done with a temperature difference, this is a model of the simplest relay, that triggered at the input value. But sooner or later we will ask ourselves the question, from how many thermometers should the value return (from one, several, all) in order for the light bulbs to light up (and also one, several or all). Address management is the association of one thermometer (or several) with one bulb (or several), where we know the position of each thermometer and each bulb. We see such a performance in physiology, where irritation of some area of the body causes a muscle spasm in this particular area of the body (or, for example, causes a complex muscle reaction as a combination and sequence of actions). But there is something similar at the population level. In particular, if the difference in temperature is the difference in values between two individuals of different types (for example, between a predator and a victim), then the actions of the victim here are like a light bulb lit up, but only one. This is unusual for us, because each light bulb is in motion, but we can assume that each individual is targeted, and if a predator has attacked the victim, then only the victim’s light bulb will light up (at the address), but not for the whole species as a whole.
Names (or addresses) never contain quantities, as a result of measurement. Even if the address is a collection of digits, it is simply a unique number, assigned to a specific control and measuring device (for example, a sensory organ) or to a specific executive mechanism (for example, a muscle cell). Therefore, an association is simply a match of names (or addresses). It does not require a separate logic for itself, the correspondence is initially thought to be constant (planned), and is configured, when designing a living being. If we have decided, that heat is beauty, and the quantity of heat is the quantity of beauty, then logic is simply, under what conditions these statements are true. More about her.
—
Each quantity conversion is accompanied by a logical condition, that allows or prohibits conversion. The most elementary condition of the transition is the logical true, there is another point, from which it is possible to form a straight line segment, which means to transfer its position to the associated straight line. Accordingly, the coordinate of point B is not essential, the main thing is that it should be greater than zero.
If we return to our example with heat, then the presence of any temperature, other than the thermometer’s own temperature (taken as zero), is a transition command. Because there is some quantity of heat, other than relative zero (temperature difference), and this is some quantity of beauty, with which we associated warmth. Nothing else is needed in this elementary version. Therefore, it can be described as a sequence of true (true — true). If it is true at the entrance, then it is true at the exit (the statement, that warmth is beauty, can be considered true). Similarly, for irritation and reaction, this is a simple relay, where any value at the input is sufficient to trigger.
In other cases, the incoming definition has a value. In the most elementary variant, the incoming value should be equal to a certain preset value, which can be called from memory every time. This is an example of a rigid condition, where the transition condition is only complete equality (input value = set value). If otherwise, then the conversion condition is, that the coordinate of point B is equal to some set value.
As a consequence, heat will be considered beauty at a strictly defined quantity of heat (a specific temperature). If there is this particular temperature — and it’s beautiful. Geometrically, this is a strictly defined straight line segment, with which the definition will be compared as a straight line segment, mathematically it is a comparison of two lengths of a straight line segment (magnitudes) or two coordinates (x) and (n) with each other. A reaction to irritation is also possible only with a certain quantity of irritation.
In a more advanced version, the condition for converting a value is set by a certain set value, which is a threshold. Accordingly, the coordinate will be converted, if its value exceeds the threshold value. This makes it possible to adjust the sensitivity, the higher the threshold value, the higher the input value for the transition should be.
For an example with heat, the threshold value will be some specific temperature. Anything above this temperature is beautiful. Geometrically, this is an incoming straight line segment, that is larger, than the established one. If the threshold value is very high, then the creature will be very rude (low sensitivity), in order for it to feel at least some sense of beauty, it will have to burn. If the threshold value is low, then it is high sensitivity. Our pampered creature will be delighted by the slightest temperature difference between itself (zero) and someone. If we remember, that the temperature difference is quite common, then the world will seem surprisingly beautiful to him, playing with different colors of beauty. What cannot be said about the rough case, where the world seems to be boring to the essence, and it is not clear, what you found in it. Similarly, for a reaction to irritation, where a high threshold value for irritation will create the illusion of insensitivity, imperturbable, unswerving, phlegmatic, etc., because a high quantity of irritation is needed to trigger the reaction. And a low threshold value will be equivalent to high excitability, explosive character, changeable mood, etc., because a small quantity of irritation is enough for a reaction.
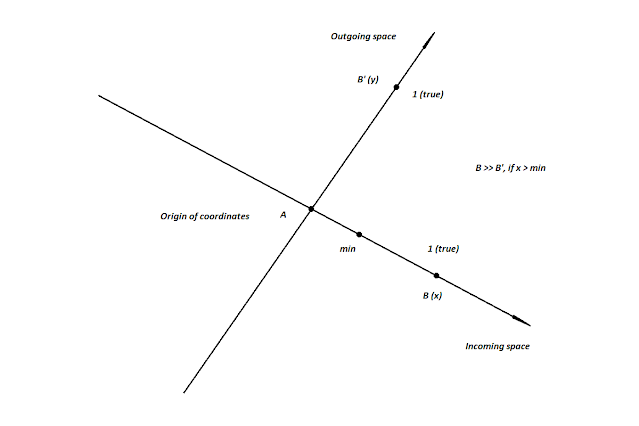
The final second option will be provided, that the transition is in the form of some range of values. Which can be considered as a straight line segment, bounded by two points. The incoming value must be above the threshold (the first is true) and below the ceiling (the second is true). If the incoming value has hit the fork (two true), then can make the transition. The threshold and ceiling are a limitation, that we are already familiar with, when a certain length of length is locked. If we consider the range as a segment, that should not be equal to zero or infinity, then the first option here will be exactly zero or infinity, because no boundaries are set (true for any coordinate, greater than zero).
 |
| This is an example, where point B will be reflected on the outgoing line, provided that its coordinate falls within the range of values (min) and (max), which is the area true on the line. |
This also makes it possible to adjust the sensitivity. The range of values can be quite wide. In this case, the creature will have a high sensitivity. Especially if the threshold value is set to the minimum. It may be narrow, in which case it will be difficult to get into it. If raise the threshold, the sensitivity will be even less. Or it can be narrowed down to just one value. Which will bring us back to the variant of the most rigid sensitivity, where for a logical true input value must be equal to a given one. If we go back to the segments, then this option will be equivalent to the zero length of the straight line segment, because the boundaries are also not set.
Thus, two boundary states are obtained. In the first state, the condition has no restrictions (walls), the creature is very sensitive, it is excited to any expression of the property. It can be said, that it is excited simply by the property. In the example with temperatures, the creature is excited simply for warmth. Its presence is enough for warmth by name at the entrance to become associated with beauty by name at the exit. Accordingly, the reaction will occur to any irritation. In the second case, the condition also has no restrictions (walls), but the creature is very selective, it is excited only by a certain expression of the property. In the example with temperatures, the creature is excited only at a predefined temperature. In a situation without walls, it is enough to have one true, the observance of which will trigger the transition. If this condition is not set, the creature will not be excited at all. Since it will not understand exactly, when (under what conditions) he can make the transition. Even if we have set up an association, that warmth is beauty, we have announced names, but the creature needs at least an elementary true, is there any warmth here and now at all. A situation without restrictions is possible, because the two boundary states are walls in themselves. The length of a straight line segment (range) is zero (a predefined specific value) or infinity (only true is enough). And inside the walls there will be another option, where the length of the straight line segment (range) is equal to some value. This case can be considered as a special case with respect to the case above.
For psychology, this is important, because the logical condition is also present in the reaction to irritation. We usually call it character. The logical condition does not define the magnitude of the reaction to irritation, but it skips or does not skip the conversion. Someone will not react even to a high quantity of irritation, and someone will react even to a minimal quantity of irritation. In physiology, this is not noticeable much, because the threshold values differ minimally. But in psychology, the threshold values can differ quite a lot, and in order for the mood to fall, a small reason is enough for someone, although for someone else this reason should be much weightier. The latter type is perceived as cold, although it’s just a small quantity of the length of a straight line segment.
—
A logical condition does not set an association, it does not set the value of the outgoing definition, although it can itself operate with incoming definitions as part of logic. The condition can be anything, but in general it boils down to just two values — true or false (enable or disable, allow the conversion of a value or prohibit). The conversion of quantities is the conversion of coordinates. To do this, we need an association (which coordinate we are converting and where), logic (under what conditions we are converting), but the digits are still the key (in distilled psychology, straight lines). Therefore, the incoming and outgoing definitions are the correspondence of two coordinates (x >> y), where there is some incoming coordinate, and there is some outgoing coordinate, the value of which is a derivative (dependent, this is a function) of the incoming one.
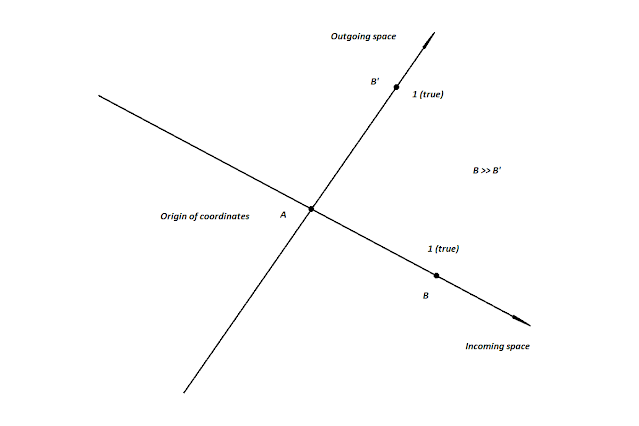
The simplest coordinate conversion is a logical conversion. The coordinate of any point on a straight line can be denoted as a digit, here such coordinates will be zero and one, which are the incoming definition of quantity. This method is similar to the inclusion logic (possible or not), but it reflects not the presence or absence of point B on the incoming line, but the position (coordinate) of point B relative to point A on the outgoing line. For example, if heat is associated with beauty, and the incoming definition returns us the coordinate true, then the quantity of heat is complete (dimensionless, infinite, it just exists), which means that the quantity of beauty is also complete. If the incoming definition returns zero to us, then the quantity of heat is zero (false in the coordinate), which means there is no beauty in it (also dimensionless, infinite, it simply does not exist).
 |
| This is an example, where point B has a coordinate (1 — true) at any distance from point A. On the outgoing line, its reflection will have the same coordinate. |
This is the return of a full or empty outgoing definition. For example, there is no one in the room, there is no beauty, the glass is full or empty, something else. They may be, but right here and now they are not. If there is, then they just are, without specifying the quantity. The outgoing definition can have only two meanings, and this is very common among dullards, where when defining it can only be black or white, always or never, good or bad, maybe or maybe not, etc., no semitones, exact quantity and other things, only yes or no. It is enough in the incoming definition to have a coordinate at least a little more than zero, and in the outgoing definition the quantity will be defined as dimensionless — this person has always been a complete idiot. In psychology, such a primitive way of conversion is not considered pathology, but it is precisely underdevelopment. In combination with the threshold values, it turns out that you can see in society at every step. For example, if the threshold value to recognize a person as a disgusting fiend is low, then the person will be recognized as a fiend completely and always for the slightest offense. Or the opposite, if the threshold value to recognize a person as valuable and filled with virtues is high, then there will be one and a half such people, but these will also be angels completely and always, no semitones. And since they still need to be found, it seems, that beauty, kindness and other virtues exist somewhere along with their carriers, but it is not possible to find them anywhere, somehow everything is wrong.
Further in the development are the digits familiar to us. In the first and also primitive case, a given value is assigned to the definition. Here, the outgoing definition is a constant, that does not change, when the value of the incoming definition changes. The incoming definition is used to start (initiate, bring to the ready state) the outgoing definition with an already set value. Therefore, the incoming definition can have any value, including logical (and this is the most rational). The magnitude of the outgoing definition never reflects the magnitude of the incoming one. In other words, subjectively the property is always expressed the same way (has a constant value), and objectively it is not expressed at all (which is false). This can be called predestination.
We will never see this in society, except in clinical cases, because this method implies an assessment, that is always the same for any actions of the person being evaluated. This is practically not present in human language, where the meaning of words can change, because this method implies a word, within which the value is always constant. This is very rarely used in physiology, when the magnitude of the reaction is strictly constant at any magnitude of the irritant. But this is very often used, when translating a real definition into an abstract one in the animal world. The smell of a predator has a constant threat value, regardless of its intensity, distance, etc., similarly for the fresh smell of prey (or the smell of fresh grass for herbivores), which has a constant saturation value. In other words, the connections in the animal world are so rigid (unambiguous), that the definition is used as identification, when the smell is a call from memory of a ready-made definition, that sets the subsequent behavior (for example, to run away, to be alert, etc.). A technical example of a rigid transformation can be an alarm system and a fire extinguishing system, where the water supply level is unchanged, and the alarm is triggered if external irritation has crossed the sensitivity threshold (sometimes it is enough to just smoke near the sensor for a shower). The animal world is organized more complicated, but the model is the same, at least some smell above the sensitivity threshold is enough to trigger.
All together can be described as two border states. At one boundary, the outgoing definition will be a specific quantity. On the other, a dimensionless quantity (true as infinity). In both cases, the incoming definition is used only to initialize some value, that is not derived from the incoming one. And then the case begins, where the internal algorithm for converting the quantity is a function, where the value of the outgoing definition depends on the value of the incoming definition. Anything can act as an incoming quantity — the result of measurement by a control and measuring device, some other incoming quantity (from other devices), a converted quantity, arbitrary, preset, called from memory, etc. But it should not be equal to zero or infinity, because in this case we are waiting for a complete uncertainty at the output. Similarly, for the outgoing value. The functions are different, but they can be generalized into three cases. In the first case, the outgoing definition is equal to the incoming definition (y = x). This is an example of a linear one-to-one relationship of coordinates, the larger the external definition, the larger the internal one.
If we return to warmth and beauty, then the temperature difference will be proportional to the difference in beauty. The higher the temperature of the other point, the more beautiful it seems. The defining point A, which produces the translation, lies on both lines (real and abstract) in the zero position. It forms a real line segment AB (capable of having a temperature, that is subjectively zero, point A is incoming lies at the origin of coordinates) with point B and an abstract AB (capable of having a beauty, that is subjectively zero, point A is incoming lies at the origin of coordinates) with a reflection of point B. In this case, the dependence is linear, so the defining point will be the point of symmetry for real and abstract reflections. The defining point knows the current coordinate of point B (what is the temperature difference), it remains to define, how beautiful it is (the difference in beauty), that is, through the function assign a coordinate to point B on an abstract straight line, here it is assigned one to one. Similarly, to translate the quantity of definition into the quantity of irritation and the quantity of irritation into the quantity of reaction to irritation. The body’s response to irritation will be proportional to the quantity of irritation. If the dependence of the water supply in the fire extinguishing system was linear on the level of smoke, then just smoking near the sensor would not be enough for a shower.
The second option is to amplify the signal by multiplying by a factor (y = k * x). In this case, the outgoing coordinate (y) increases by this factor relative to the incoming coordinate (x). Or decreases if the coefficient is less than one, but it is still a linear relationship. The coefficient can be set as a constant, then the distortion will be constant. An even more pronounced amplification is the exponentiation of the incoming definition (y = x ^ k), in this case the dependence will cease to be linear.
 |
| This is an example, where the coordinate (x) of point B is reflected on the outgoing line in proportion to the coefficient (k) or exponentiation (k). This is an incoming signal amplification model. |
A more complicated option is, if the coefficient is some kind of incoming definition, in this case the distortion will depend on the value of the variable, taken as a coefficient. If it also comes from some kind of control and measuring device, then the outgoing value will be derived from two properties at once (or so). For example, the quantity of beauty depends not only on the quantity of warmth, but also on the illumination. The higher the illumination, the more beautiful, even if the temperature difference has not changed. For a change, it can be two different addresses for one property. In practice, this technique is used when converting a definition into irritation, which depends on distance, for example, the degree of threat of a predator to the victim is constant, but the feeling of fear depends not only on this value, but also on the distance to the predator. If the dependence of the water supply in the fire extinguishing system is linear on the level of smoke, and just smoking near the sensor is no longer enough for a shower, then need to apply a coefficient, because smoking is harmful and dangerous.
The third option is to extinguish the signal through a ratio with a given coefficient (y = k / x). If the coefficient is constant, then this is a pure inverse relationship, since the distortion of the outgoing value is constant. The larger the incoming definition, the smaller the outgoing definition.
In our example, the hotter, the uglier. But the ice is the ideal of beauty. In a more complex version, the coefficient can also may be defined. Then the outgoing definition will float relative to the two incoming ones. In our example, should be very light and very cold to make it very beautiful. But in the cold dark, somehow not very much. Or the higher the danger, the quiet need to behave, so as not to attract attention. If the dependence of the water supply in the fire extinguishing system is the reverse of the level of smoke, then to turn off the shower will have to smoke near the sensor constantly and in a crowd.
The functions are different, so there can be many conversion options. If the creature has a memory, in which the previous definitions are written, then can call them from memory. We are can to add several of incoming or outgoing variables, if necessary, or several of coefficients. But there is a minimum requirement, that at least one value of the incoming definition corresponds to one value of the outgoing definition, at least one incoming name (or address) is associated with one outgoing name (or address), and at least one condition, under which conversion is allowed. And in conclusion, about what no one forbids us to do, but it will have consequences.
If the coordinate is converted one to one, then we won’t see any effects. But if at least in one conversion the incoming and outgoing coordinates are different, then with each cycle the definition will increase or decrease. This is an example of recursion (usually called positive or negative feedback), the function for the definition calls itself. This method is very widely used in psychology to extinguish the signal. Any recursion, if it does not have a forced exit, has a natural exit — near zero or near infinity (zero and infinity themselves are unattainable here). For example, if the quantity of water supply in the fire extinguishing system depends on the level of smoke, and the quantity of smoke depends on the quantity of water supplied. The higher the smoke, the greater the quantity of water supplied, but the greater the quantity of water supplied, the less smoke (extinguishing), where the final result will be zero smoke and zero quantity of water supplied. Psychological organization is performed more efficiently, so we do not see recursion in the opposite direction. But the social organization is performed less qualitatively, so instead of extinguishing the signal, sometimes there is an increase to its natural maximum (self-excitation). Maybe, somewhere it was thought that way, but in general it should not be done that way.
—
Definitions have orders, this is the difference of values after comparing the current and previous values. The previous value needs to be remembered somewhere, which requires memory in which both the results of previous measurements and the results of operations with measurement results will be stored. Without memory, the creature will operate only with up-to-date information. If the creature has a memory, then other information can be stored there. Memory has a feature — it is not rubber. Therefore, it needs not only to be filled, but also cleaned. The simplest option is to delete information from memory, if it is no longer needed. Here, the variable itself, to which this value is assigned, can go into oblivion along with the spent value. Therefore, there is a more complicated option, to change the value of a variable from one (no longer relevant) to another (more relevant). In the latter case, it is also a conversion of a quantity, including a set of conditions for the conversion. All data can be divided into four types. The first are those variables, whose value can be changed with each call to the default definition. Simply put, the variable A in each act is equal to a new value. The second are those variables, whose value can be changed, only if the conditions are met. For example, if B is equal to (greater than, less than) C, then A is equal to the new value. The third are those variables, whose value sets the conditions, and these values can also be changed, only if the conditions are met. For example, if D is equal to (greater than, less than) E, then B or C are equal to the new value. Accordingly, the value of the variable A can then be transformed already under other conditions. This is very widespread in human language and human society. And the fourth are those variables, whose magnitude cannot be changed.
—
The result is a technical device for converting quantities, which we call a living being. It accepts information at the input and returns it at the output. It also knows, how to identify incoming information. In a primitive form, this is a model of the simplest association, when the presence of true at the input includes true at the output. For example, if the intensity of illumination is associated with the sound of a siren, then any illumination will return true (it is), the siren will scream non-stop, reducing activity only at night, when the illumination returns false (too dark). In a more progressive form, this control of the volume of the siren sound is proportional to the quantity of illumination. There are only two unusual points here. Firstly, the association is made with an abstract property, and only then with the work (reaction to the irritant). Lighting is beautiful, and the intensity of lighting is the quantity of beauty. It is not from the lighting, that the siren will scream, if we highlight it, but from the beauties, that have opened up to it. Thereby turning from a simple relay into a psychological subject, because illumination has an additional meaning (value) for her. Secondly, the specificity of psychology and analytical geometry, which require the device to have internal parameters of lighting, beauty and sound level, and these parameters are always zero. If the quantity of illumination is equal to the internal parameter of the siren, then it will not scream, because there is no difference in values, so there is nothing beautiful, so there is no work (reaction to the irritant). Beautiful is more or less, than me (her preset illumination parameter).
—
Previous chapter — Defining a point in an abstract space
—
Next chapter — Mathematical point
—











Comments